Stop Arc Flash: Complete Workplace Safety Guide
Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) violations in 2022
Capable of causing severe burns, injuries, and fatalities
Arc flashes release immense energy in the form of intense heat, blinding light, and powerful pressure waves, capable of causing severe burns, injuries, and fatalities. These incidents underscore the critical need for rigorous safety measures in industrial settings. Implementing comprehensive safety protocols, including proper training, hazard assessments, and the use of appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), such as arc-rated clothing and face shields, is essential to mitigate risks effectively.
Occupational fatalities due to contact with electricity account for approximately 9% of all deaths in the construction industry and is the fourth leading cause of death in this industry.
Arc Flash Training Online
By prioritizing Arc flash safety and compliance with regulatory standards and emphasizing arc flash training online, organizations can safeguard workers’ well-being and protect equipment integrity from the devastating effects of arc flashes.
Understanding Arc Flash
An arc flash occurs due to electrical faults, often stemming from equipment failure, improper maintenance, or human error. Shockingly, statistics reveal that arc flash accidents happen daily, underscoring the urgent need for robust safety protocols and preventive measures. These incidents highlight the unpredictable nature of electrical hazards and emphasize the importance of comprehensive safety strategies.
Arc Flash Safety Standards
Compliance with the NFPA 70E Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace is paramount. Section 120.5 of NFPA 70E outlines the process for establishing an electrically safe working condition, emphasizing the importance of proper procedures and precautions to prevent arc flash incidents. By following these guidelines and implementing best practices, organizations can effectively reduce the risk of electrical hazards and ensure the safety of all workers involved in electrical operations.
Regulatory bodies like the NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) play a crucial role in establishing and enforcing guidelines to mitigate the risks associated with arc flashes by providing different OSHA arc flash programs in industrial settings. Arc flash incidents pose a significant hazard to electrical maintenance personnel due to the sudden release of energy, capable of causing severe injuries and fatalities.
Adherence to regulatory standards is not just a legal requirement but also fundamental in creating a safe working environment. These standards mandate the use of appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), training programs, arc flash certifications, and safety protocols tailored to mitigate the specific risks of arc flashes.
Ensuring compliance means workplaces are adequately equipped with necessary safeguards and measures to protect against electrical hazards. By prioritizing safety, staying up-to-date with industry regulations, and providing employees with online arc flash training, organizations can minimize the likelihood of arc flash incidents, promote worker safety, and uphold operational integrity.
Key Factors Contributing to Arc Flash Incidents
arc flash safety

Electrical arc flash safety
Human Errors
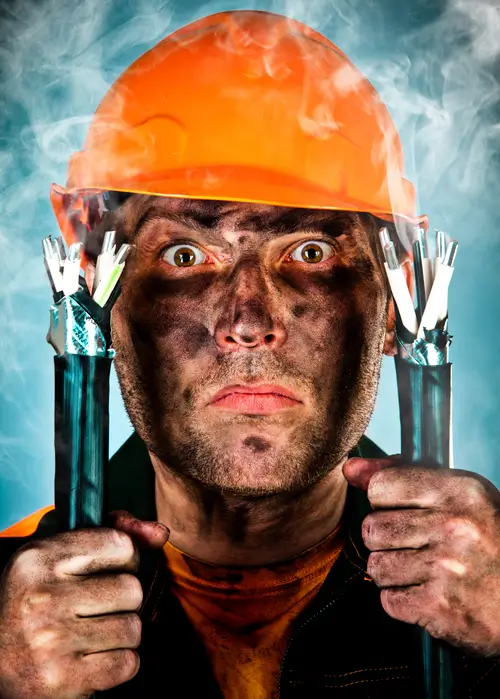

Human Errors
Flash Incidents
Flash Incidents
Work Safely

Work Safely around Electrical Equipment
Arc Flashes
Arc Flashes
Arc Flash Safety Measures

Administrative Controls: Administrative controls encompass comprehensive safety protocols, training programs, and hazard assessments designed to educate workers about the risks of arc flashes and establish clear procedures for response and evacuation. Regular safety audits, emergency drills, and continuous training sessions ensure that employees are well-prepared to handle potential arc flash incidents. By integrating administrative controls into daily operations, organizations can develop a culture of safety and reduce the likelihood of workplace accidents (NFPA).
Appropriate Training

Training
One of the most efficient ways to protect workers from this hazard is by providing them specialized training. By enrolling workers into training like Electrical Arc Flash Awareness Online Course, you can increase their knowledge about the Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) that are generally applied to prevent injuries due to arc flash.
PPE

Training
Properly rated PPE plays a pivotal role in protecting workers from the harmful effects of arc flashes. Arc-rated clothing, gloves, face shields, and helmets are designed to withstand the intense heat and potential projectiles of these incidents. By wearing appropriate PPE, workers can significantly reduce the severity of injuries and increase their chances of safely evacuating the area during an arc flash.
Arc Flash Boundary Labeling

Boundary Labeling
While there are no specific OSHA arc flash labeling requirements, clearly marking arc flash boundaries with signage and labels is crucial for enhancing workplace safety. These visual indicators alert workers to specific danger zones where arc flashes could potentially occur, prompting them to maintain safe distances and adhere to safety protocols. By providing clear guidance, personnel can take necessary precautions when working near energized equipment, minimizing the risk of accidental exposure to arc flashes.
This proactive measure not only increases awareness of potential hazards but also reinforces a culture of safety, ensuring that employees are well-informed and empowered to prioritize their safety while performing their duties.
How to Protect Yourself from Arc Flash
To protect yourself from arc flash, wear appropriate PPE (flame-resistant clothing, face shields, gloves), follow NFPA 70E guidelines, and de-energize equipment before working. Maintain a safe distance, use insulated tools, and undergo proper safety training. Regularly inspect and maintain electrical systems to prevent hazards.
The Case of Jason Brozen
Protecting ourselves from arc flashes is paramount due to the severe and life-altering consequences they can inflict. Jason Brozen’s experience vividly illustrates this danger. Despite his extensive experience as a master electrician, an arc flash incident in 2009 left him with third-degree burns on his face and arms. The trauma of the incident not only resulted in physical injuries but also led to a week-long coma and two weeks in intensive care. This case underscores the critical need for strict adherence to safety protocols and the use of protective measures like PPE and engineering controls to minimize the risk of such catastrophic events in electrical work settings.
Engineering Controls

Engineering Controls
Engineering solutions such as arc flash mitigation systems and enhanced equipment design are critical in minimizing the impact of arc flashes. These controls aim to limit the energy released during an incident and prevent the spread of electrical faults. Investing in advanced engineering technologies and retrofitting existing systems with protective measures can effectively mitigate the risks associated with arc flashes.
Predictive Maintenance Techniques

Predictive Maintenance Techniques
Techniques like infrared thermography and ultrasonic testing are proactive strategies that play a crucial role in preventing arc flash incidents. These methods detect subtle changes in equipment temperature, vibration, or sound, signaling potential faults before they escalate. By swiftly addressing these early indicators of deterioration, organizations can preemptively repair or replace faulty components, thereby reducing the risk of equipment failures that might trigger arc flashes.
This approach enhances operational reliability and promotes a safer work environment by mitigating the likelihood of unexpected electrical hazards and ensuring that systems remain in optimal working condition.
Remote Racking Systems

Remote Racking Systems
These systems are crucial safety tools in industrial settings, enabling operators to manipulate circuit breakers from a safe distance. By eliminating the need for direct physical interaction with energized equipment, these systems significantly mitigate the risk of arc flashes during maintenance or troubleshooting tasks.
Operators can engage and disengage circuit breakers remotely, reducing exposure to hazardous electrical components and enhancing overall worker safety. This technology not only minimizes the potential for accidents but also ensures that personnel can perform essential tasks with heightened safety and efficiency, promoting a safer working environment.
How to Prevent Arc Flash
Implementing best practices for arc flash prevention involves conducting regular equipment inspections, performing detailed risk assessments, and maintaining stringent maintenance schedules to identify and mitigate potential hazards. Establishing a robust arc flash risk management program tailored to the unique needs of the workplace ensures that all safety measures are consistently applied and updated to reflect industry best practices. By promoting a proactive approach to safety and developing a culture of awareness through arc flash training certification, organizations can effectively minimize the risks associated with arc flash and create a safer work environment for all employees.
Conclusion
Prioritizing arc flash safety is not only a legal obligation but also a moral imperative to protect the lives and well-being of workers involved in electrical operations. By investing in comprehensive safety measures, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with arc flashes and safeguard their workforce from potential harm. Continuous education, adherence to safety protocols, and proactive risk management are essential components of a successful arc flash safety program. Together, these efforts contribute to a safer workplace and ensure that employees are adequately prepared to respond to and prevent arc flash incidents effectively.








